Best spleen doctor in delhi
What is Laparoscopic Splenectomy?
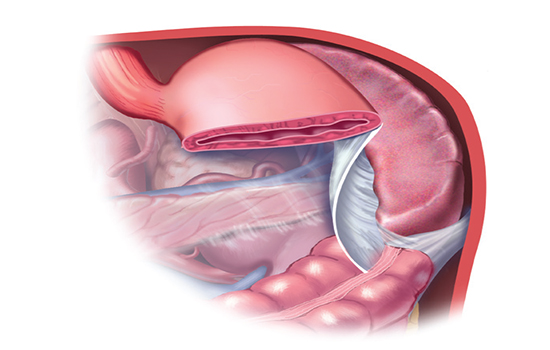
Splenectomy is the surgical procedure where the infected or diseased spleen is removed. The spleen is located just behind the left rib cage The spleen’s major role is to fight infections and filter out old and damaged blood cells. The major reason for spleen removal is once there is a disease involving the spleen, or if the spleen is ruptured due to trauma and is bleeding inside. Dr. Saggu is the best spleen specialist doctor in Delhi.
This procedure can be done by a keyhole technique called a laparoscopic splenectomy.
What are the Causes of Splenectomy?
- Autoimmune diseases of the spleen
- Blood disorders
- Benign tumors of the spleen
- Trauma
- Enlarged spleen
- Splenic cysts
- Selected leukemias and lymphomas of the spleen
What is the procedure for a laparoscopic splenectomy?
After you have been given anesthesia, the surgeon will insert the laparoscope into your abdomen by making an incision. Carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdomen via another incision to give the surgeon more space to operate. The spleen is then separated from the other organs and removed. The incisions are closed after the procedure is completed. A drain tube may be left in place to enable fluid to drain from the surgical site. This is often eliminated within a few days.
What are the Contraindications for Laparoscopic Splenectomy?
Because intra-abdominal bleeding interferes with the surgeon’s ability to view the blood vessels and splenic attachments, laparoscopic excision of the spleen is not indicated in situations of trauma. Spleens that are enormously enlarged may also provide a challenge for the surgeon since the size of the spleen limits the surgeon’s ability to see and manipulate the spleen. Portal hypertension is usually another contraindication to any type of splenectomy.
What are the post-surgery precautions for a splenectomy?
When performed for elective indication laparoscopic splenectomy is typically a safe procedure. In an emergency setting like in trauma with massive bleeding, it is done as a life-saving procedure.
The spleen is important in the formation of immunity. As a result, unless necessary, splenectomy is normally avoided in children. One week before the procedure, the patient is given specific immunizations. Minor infections, such as sore throats and fevers, should be avoided after splenectomy since they might flare up suddenly. Get advice from our spleen specialist doctor in Delhi Dr. Sukhvinder Singh Saggu.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What happens if your spleen is removed?
Ans. Being active without a spleen is possible, but you are at greater risk of getting ill or serious infections. The highest risk occurs shortly after the surgery. Individuals without a spleen may encounter greater difficulties recovering from illness or injury.
- Is splenectomy life-threatening?
Ans. Splenectomy is performed to remove an inflamed or damaged spleen. When removed, other organs, such as the liver, start taking over the functions helping patients cope with the infections. However, the risk of developing severe disease remains for a lifetime.
- Can humans live without a spleen?
Ans. The spleen is a fist-sized organ in the upper left of the abdomen, next to the stomach, and behind the left ribs. It’s an integral part of the immune system that helps fight infections and diseases. An enlarged or inflamed spleen is necessary to remove. One can survive without it as the liver can take over many of the spleen’s functions.
- What are the benefits of spleen removal?
Ans. Spleen removal is major surgery and leaves patients with a compromised immune system.
Splenectomy can effectively address various health problems that cannot be resolved through other treatments, including blood disorders, cancer, and infections. Removing a ruptured spleen can save a patient’s life as the liver works as an alternative in managing some of its functions.
- What is the best food after spleen removal?
Ans. After splenectomy, one may start to feel full quickly. Eat bland, low-fat foods like plain rice, bananas, oatmeal, baked potatoes, broiled chicken, toast, and yogurt. Avoid dairy products other than yogurt containing live cultures called probiotics. Some may be advised to take iron supplements. Drink plenty of fluids to avoid becoming dehydrated.
